Category Definition
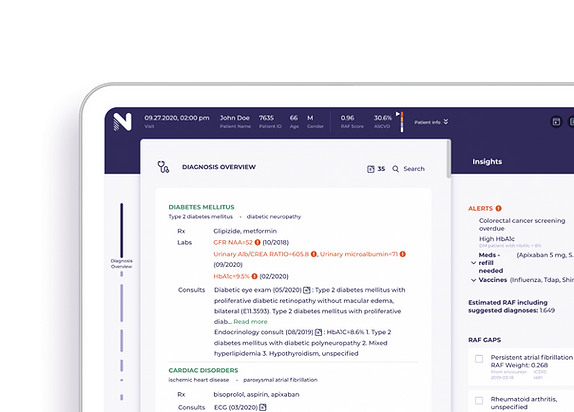
This category of AI Assistants helps clinicians review across all disparate records and summarize the patient’s history and care to support their current visit. The AI Assistant reviews the entire chart and accessible records including; labs, diagnostics, referrals, consult notes, discharge summaries, scanned documents and provides them a problem-oriented summary of the chart. The AI Assistant eliminates the need for the clinician to search and click through the records and manually collect and summarize new information and pertinent changes. The AI Assistant does it for them in seconds and creates a problem-oriented summary identifying missing diagnoses and gaps in care..
Impact
Evaluation of Impact (n=10)
-
61% decrease in physician visit prep time
-
38% increase in HCC scoring*
-
23% increase in found diagnoses*
Evaluation of adoption (n=58)
-
38% reduction in visit preparation time
-
45% increase in feeling better prepared
-
29.5% reduction chart review burden
-
23% reduction burnout (Maslach)
-
22% increase practice satisfaction
Use of AI Recommendations (n=1836, 683k visits)
-
Reviewed summary in 85% of visits
-
Addressed 87% of the time
-
Accepted 84% of the time
-
Rejected 9% of the time
Collective Voice
When I saw it, I felt my brain uncoil.
When I used it was an obvious game changer.
I went from “definitely burning out” to “under stress but not burned out".
How can you place a price on a missed diagnosis?
It helps me be fully present in the visit.
I definitely feel more hopeful now.
It has really decreased frustration, number of clicks and gave clinicians back time.
My time and effort have been really decreased.
My average review time went from 10 min to 2 min on complex patients).
I feel like I have an extra pair of eyes on my chart, all the time, helping to make sure I don’t overlook a critical piece of data."
We are an ACO and so it really helps our physicians capture the appropriate
level of care and HCC coding on patients.
We’re closing those care gaps and capturing those HCC codes
and getting credit for the patients that we’re seeing.
Characteristics
Visit Preparation
Physician gain time, as cognitive and administrative burdens are dramatically reduced. They review the most essential information that were submerged in overwhelming amounts of patient data. They can search quickly, explore files, and gain one-click documentation capabilities, improving efficiency for the entire care team.
Generate Patient Summary
AI organizes data from multiple sources, enabling clinicians to quickly act to maintain and improve their patients’ health status. These contextual insights ensure high levels of user-engagement that lead to better care and value based outcomes.
Risk Adjustment
Effective risk adjustment requires accuracy. Assistant leverages multi-source structured and unstructured data from EHRs, HIEs, claims, imaging, and labs to drive evidence-based insights in the moment of care. Our seamless risk adjustment workflow reduces the burden on coders and physicians resulting in high engagement.
Clinical Recommendations
Assistant produces clinical alerts for medication refills and lab abnormalities, as well as recommendations for vaccines, screenings, and more,
How it assists in documentation (by GPT4)
Alright, let's dive into how a tool like Navina's AI assistant can support healthcare professionals. I'll use a story format to make it relatable and easily understood.
Meet Dr. Emily - a busy primary care physician.
1. Chart Review and Visit Preparation:
-
Before AI: Each morning, Dr. Emily spends hours poring over multiple patient files, noting histories, and understanding what needs to be addressed during the day's appointments. It's time-consuming and, sometimes, crucial details might slip through the cracks.
-
With AI: As Dr. Emily enjoys her morning coffee, the AI assistant provides a summarized view of each patient's medical history, recent tests, medications, and previous concerns. When Mr. Thompson walks in, she already knows he had an elevated blood pressure reading last month and has been on new medication since.
2. Finding and Recommending Diagnoses & Suspected Conditions:
-
Before Navina: When Mrs. Rodriguez complains of fatigue and joint pain, Dr. Emily has to rely on her memory, experience, and perhaps some manual research to consider all potential diagnoses.
-
With AI: The AI scans Mrs. Rodriguez's entire medical history and compares it with medical databases. It suggests that, based on her recent weight gain, family history of thyroid issues, and current symptoms, she might have hypothyroidism. This doesn't replace Dr. Emily's expertise but serves as an informed second opinion.
3. Improving HCC Coding and RAF Scoring:
-
Background: HCC (Hierarchical Condition Category) coding is a system that categorizes patients based on their illnesses and conditions. RAF (Risk Adjustment Factor) scoring helps determine the predicted costs for caring for a patient for the next year.
-
Before: After seeing a patient, Dr. Emily would hand over her notes to a medical coder or do the coding herself. It's a nuanced job; missing or inaccurate codes could mean less funding for patient care.
-
With AI: After seeing Mr. Thompson, the AI assistant cross-checks his conditions with HCC coding guidelines. It recognizes that his hypertension, combined with his age and recent elevated cholesterol levels, places him in a specific HCC category. The AI then calculates an RAF score indicating he might need more medical attention (and therefore resources) next year. This ensures the clinic gets the appropriate funding for Mr. Thompson's care.
Imagine the AI Assistant as Dr. Emily's super-organized assistant. Before the day starts, it lays out key patient details, almost like preparing a cheat sheet for an exam. Throughout the day, it whispers possible diagnoses based on everything it "knows" from vast medical databases. And at the end of the day, it ensures every patient's conditions are correctly "labeled" so that the clinic gets the right amount of money to care for them in the coming year.
How the AI works (by GPT4)
Here is a break down the components of the AI engine that powers an AI Assistant for clinical review and value-based care:
Data Integration:
-
This tool gathers data from various sources and combines it into one unified view.
-
It's like having a medical team (nurse, radiologist, pharmacist, etc.) each presenting their findings in a morning huddle, ensuring you have a full picture of the patient.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
-
Enables the AI to understand human language from medical records, notes, and other text sources.
-
It's as if the AI has been trained in medical terminology. Like a new resident who quickly learns to interpret medical jargon, the AI "reads" and "understands" the patient notes and histories.
Machine Learning (ML):
-
A feature that helps the AI learn from existing data and improve its recommendations over time.
-
Picture ML as a doctor's clinical experience. Just as a physician becomes more adept with diagnosis and treatment over years of practice, ML helps the AI refine its suggestions based on patterns it has seen before.
Predictive Analytics:
-
Algorithms that forecast potential future outcomes based on current data.
-
This is like epidemiology for individual patient care. Just as epidemiologists predict disease outbreaks based on current data, predictive analytics forecasts individual patient risks or health trajectories.
Decision Support Systems:
-
Provides evidence-based recommendations to aid clinical decision-making.
-
Think of it as having a specialist consultant on standby 24/7, offering guidelines or advice on specific cases based on vast clinical research.
Feedback Loop:
-
The AI learns from feedback, refining its suggestions and improving accuracy over time.
-
It's similar to morbidity and mortality (M&M) conferences where physicians review cases to determine what went well and what could be improved, refining their future approach based on past outcomes.
Security and Privacy Protocols:
-
Measures that ensure patient data remains confidential and protected.
-
It's akin to the healthcare protocols that ensure patient confidentiality and HIPAA compliance, ensuring the AI handles data with the utmost care.
By meshing all these components together, an AI engine can efficiently assist in clinical review and value-based care. It's as if a physician has a team of specialists, data scientists, and medical librarians at their beck and call, all working in tandem to provide the best patient care recommendations.
Products
There is a growing number of companies now saying they are providing AI Assistants to help capture missing diagnoses and HCC coding. We intend to develop tools to help physicians to evaluate offerings in this category and make a decision informed by the in-practice experience of “physicians like them”. Here is list of companies with products that may be in this category:
- TBD
Lab Partner: Navina
Navina is a leading innovator of AI driven clinical review. They partnered with family medicine and primary care practices to develop the AI assistant functionality to support clinical review, chart review, and visit preparation. Navina’s reason for being is well aligned with the goals of the lab; helping physicians primarily care for their patients. The company is actively and successfully deploying their solution to primary care and family medicine physicians. The solution is readily adoptable, software only, not requiring any new hardware. The Innovation Lab with the Navina Digital Assistant was conducted on the eCW EHR and athenaOne EHR. This was based on the fact that this AI assistant was already being used by family physicians with these EHRs.